A large part of the CISO/CIO responsibility is ensuring compliance standards are met. As one of the main drivers of security product purchase and implementation, regulation comes in many different shapes and sizes. Some standards provide clear consequences for failure to meet them. Others provide more of a guidance approach as to what the organization should do. The Comprehensive Security Guide (download here) gives organizational security leaders a document comprised of standardized and user-friendly templates that guide them through assessing their compliance with all the main regulation frameworks: PCI-DSS, HIPAA, NIST Cyber Security Framework and GDPR.
Frequently organizations employ an independent auditor to assess their regulation compliance. But prior to this, it is smart for security stakeholders to carry out their own gap analysis of the environment in respect to the standards they want to meet.
With the Comprehensive Compliance Guide, security leaders save the expenditure of time and resources which they might otherwise put into creating their own compliance evaluation methods. Rather than building the standards matrix from zero or searching for free templates online, CISOs can utilize this tool to access a document providing all compliance guidance in one. And while many organizations will not need them all, it is probable that at least one of the standards guides will prive useful.
Assessment templates for the following standards are included in the compliance guide:
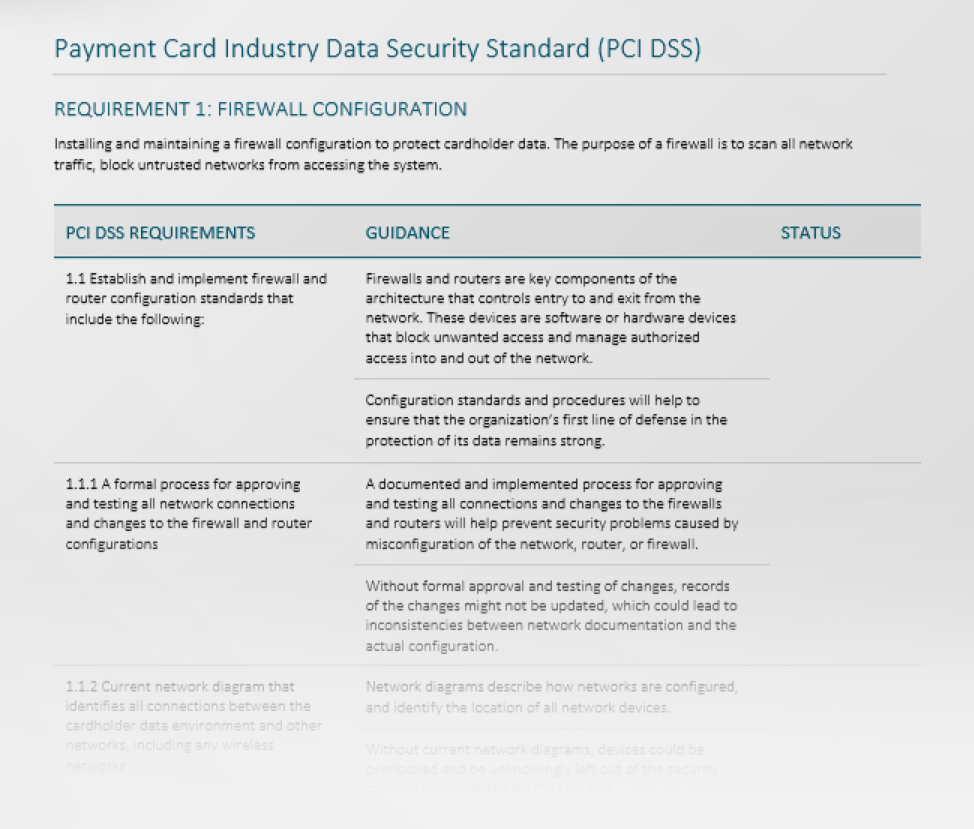
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
Every organization dealing with branded credit cards from the major card providers needs to meet this standard. Not meeting the PCI DSS standards opens the organization to lawsuits that arise when breaches take place, compromising card data.
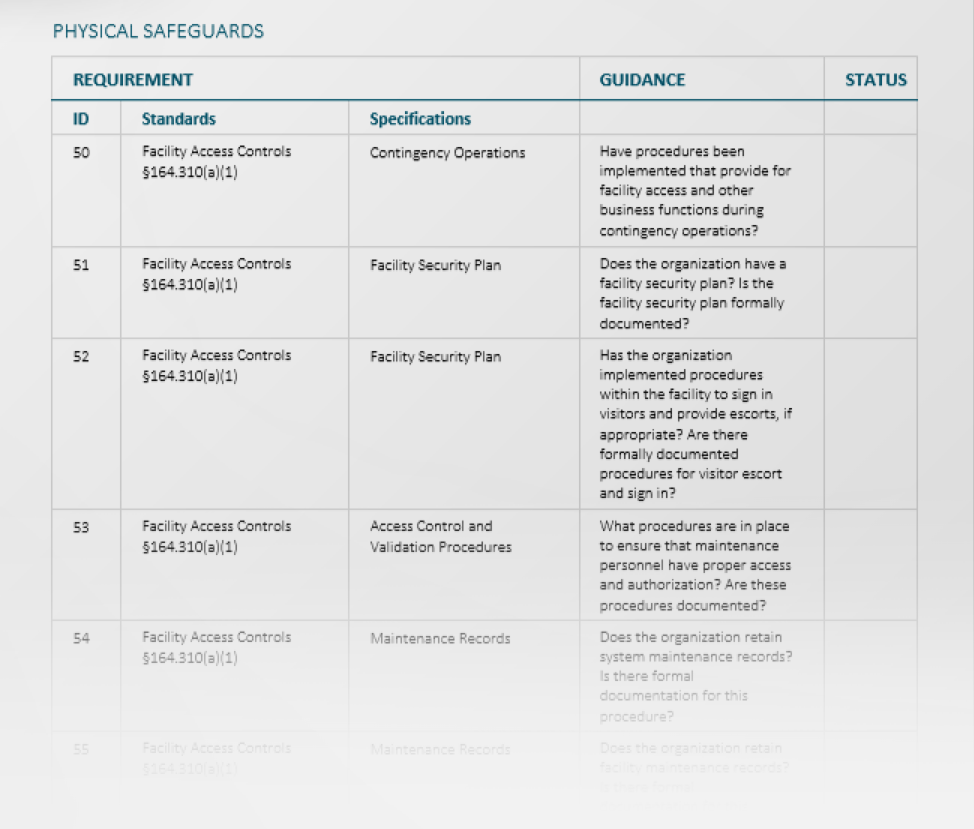
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
The data privacy and security concerns of medical information were at the forefront when the US passed the HIPAA legislation. All bodies operating within the healthcare industry – which is highly susceptible to cyberattacks – are expected to meet these standards: hospitals, medical centers and health insurance providers.
- NIST Cyber Security Framework (CSF)
Computer security guidance for organizations in the private sector, helping them assess and improve their prevention, detection and response to cyberattack. All organizations are included and it is not confined to one specific vertical, but at the same time, this is not a binding regulation. Together with this, it is quickly becoming the go-to standard, and organizations adopting it are seen as practicing sound security. - The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The privacy and data of all individuals of European Union (EU) / European Economic Area (EEA) citizenship are protected by GDPR standards. This also includes the transfer of personal data outside of the EU / EEA and covers every organization that stores / processes the PII pf European Union citizens. Fines for failing to meet these standards can reach 5% of the violating body’s annual revenue.
CISOs and other security executives can utilize the guide to quickly and easily map the compliance framework that is the best fit for their organization. This includes allowing the launch of internal assessments of their environment, with rapid results and the delivery of clear, insights on what actions are recommended.