There are five vulnerabilities fixed in the latest release of the Apache Web server, including a buffer overflow and several denial-of-service vulnerabilities. Fixes for these flaws have landed in the developer release of the server, 2.4.10-dev.
The buffer overflow vulnerability is rated moderate by the Apache Software Foundation, but it could be used for remote code execution under the right circumstances. The flaw lies in the way that Apache handles updating the mod_status component. It’s caused by a race condition, and an attacker can exploit it without authentication.
“The specific flaw exists within the updating of mod_status. A race condition in mod_status allows an attacker to disclose information or corrupt memory with several requests to endpoints with handler server-status and other endpoints. By abusing this flaw, an attacker can possibly disclose credentials or leverage this situation to achieve remote code execution,” says the advisory from HP’s Zero Day Initiative, which reported the vulnerability to Apache on behalf of the researcher who discovered it, Marek Kroemeke.
Apache’s advisory says that an attacker would need the right conditions in order to exploit this vulnerability.
“An attacker able to access a public server status page on a server using a threaded MPM could send a carefully crafted request which could lead to a heap buffer overflow. Note that it is not a default or recommended configuration to have a public accessible server status page,” Apache’s advisory says.
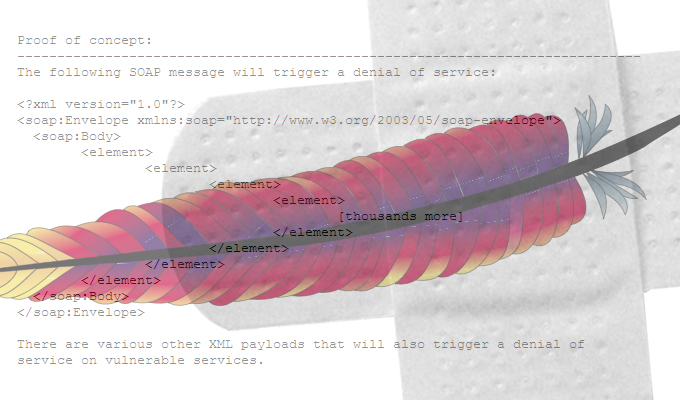
Along with the buffer overflow, there are four DoS vulnerabilities fixed in 2.4.10. Two of those vulnerabilities are rated important and the other two are considered moderate risks.