Researchers are warning a recently discovered and highly critical vulnerability found in Drupal’s CMS platform is now being actively exploited by hackers who are using it to install cryptocurrency miners and to launch DDoS attacks via compromised systems. At the time of the disclosure, last month, researchers said they were not aware of any public exploits.
Now Netlab 360 researchers say they have identified a botnet, dubbed Muhstik, that is taking advantage of the Drupal bug. They said multiple scans on infected Drupal instances reveal attackers are exploiting the vulnerability by accessing a URL and then injecting exploit code. The technique allows adversaries to execute commands on targeted servers running Drupal.
The Muhstik botnet exploits Drupal vulnerability (CVE-2018-7600), impacting versions 6,7, and 8 of Drupal’s CMS platform. “This potentially allows attackers to exploit multiple attack vectors on a Drupal site, which could result in the site being completely compromised,” warned MITRE’s Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures bulletin on March 28.
Drupal, which also released a patch for the vulnerability in March, warned that over one million sites running Drupal are impacted. Unprivileged and untrusted attackers could also modify or delete data hosted on affected CMS platforms, Drupal said.
After further investigations, Netlab researchers said that it believes at least three groups of malware were exploiting the vulnerability.
“We noticed one of them has worm-propagation behavior. After investigation, we believe this botnet has been active for quit a time. We name it Muhstik, for this keyword keeps popup in its binary file name and the communication IRC channel,” wrote Netlab 360 researchers.
According to Netlab, Muhstik is a variant of Tsunami, a malware strain that creates botnets with infected Linux servers and Linux-based IoT devices.
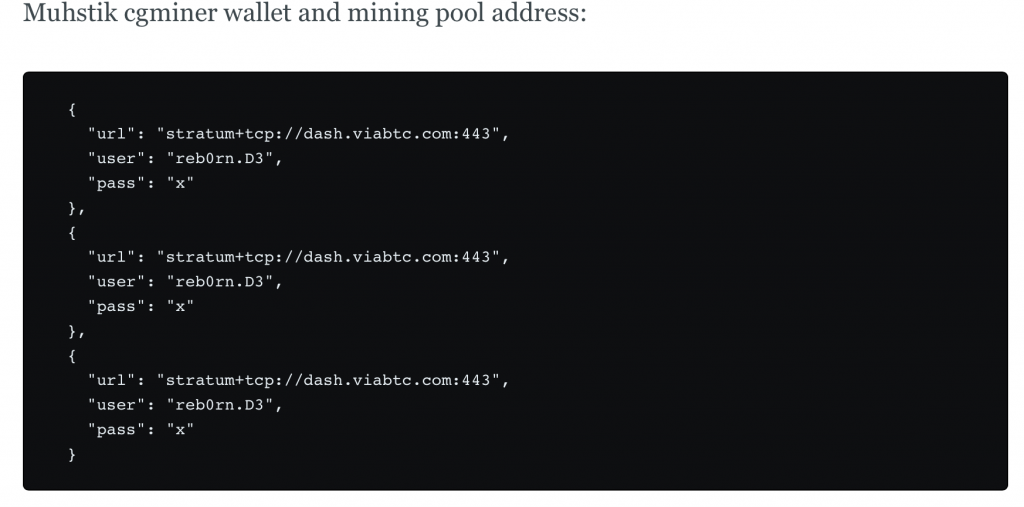
Muhstik has the capability to install two coinminers – XMRig (XMR) and CGMiner – to mine the open-source, peer-to-peer Dash cryptocurrency, according to Netlab.
Researchers say the botnet uses the open-source XMRig utility to mine cryptocurrency with a self-built mining pool (47.135.208.145:4871). Meanwhile, it uses popular mining software CGMiner to to dig cryptocurrency coins using multiple mining tools (with username reborn.D3), they said.
In addition Netlab researchers said they intercepted multiple DDoS attack instructions targeting the IP address 46[.]243[.]189[.]102.
Muhstik relies on 11 command and control domains and IP addresses, and the attackers also uses the IRC communication protocol to invoke commands for the botnet: “We observed multiple IRC Channels, all starting with ‘muhstik,'”said Netlab researchers in a report. “At present, we can not confirm which specific channels are open on which C2 server. This is due to the characteristics of the IRC protocol itself. Only when we receive a communication instruction from the corresponding channel can we confirm it’s present.”
Muhdtik also has capabilities to scan for vulnerable server apps using the the aiox86 scanning module. This module “scans TCP port 80, 8080, 7001, 2004, and tries varieties of different payloads on each port,” according to NetLab.
GreyNoise Intelligence said in a tweet that it detected the botnet to be exploiting a vulnerability (CVE-2017-10271) in Oracle WebLogic Server as well, indicating that Muhstik is exploiting vulnerabilities in other server applications.
UPDATE: there is a 95% overlap between the IPs scanning for the previously reported #drupalgeddon vulnerability and the Oracle CVE-2017-10271 vulnerability.
— GreyNoise (@GreyNoiseIO) April 18, 2018
Troy Mursch, founder of Bad Packets Report, told Threatpost that given the criticality of the exploit and the repurcussions once it’s used, “the race is on to find vulnerable Drupal installations.”
“I recommend affected users update to Drupal 7.58 or 8.5.1 as soon as possible. To note as well, updating to the patched version doesn’t retroactively ‘unhack’ your site. I recommend website operators check their installation (server) for any of the IoCs mentioned in the 360 Netlab report after completing the update,” he said.