A cyber-espionage malware has been discovered that’s capable of collecting and exfiltrating sensitive documents from within air‑gapped networks.
The malware, dubbed Ramsay, is still under active development — so far, researchers have found three different samples, with each sample adding new features. However, Ramsay’s targeting of air-gapped networks make the toolkit a formidable threat, researchers say. An air gap is a security measure to ensure that computer networks are physically isolated from other, potentially unsecured networks (such as the public internet or an unsecured local area network).
“Some stages of Ramsay’s framework are still under evaluation, which could explain the current low visibility of victims, having in mind that Ramsay’s intended targets may be under air-gapped networks, which would also impact victim visibility,” said researchers with ESET in a Wednesday analysis.
Researchers initially found an instance of Ramsay in VirusTotal, in a sample uploaded from Japan. The timestamps for the malware’s components imply that its framework has been under development since late 2019. The malware shares many artifacts with Retro, a backdoor malware associated with DarkHotel, a notorious APT group known to have conducted cyber-espionage operations since at least 2004 that has targeted government entities in China and Japan previously.
Infection
The Ramsay samples discovered by researchers have been leveraged in real-life attacks using multiple attack vectors. One of these is malicious RTF documents, while another was a binary masquerading as a 7zip installer. Once opened, these attempt to exploit a remote code execution vulnerability in the system (CVE-2017-0199), which exists in the way that Microsoft Office and WordPad parse specially crafted files.
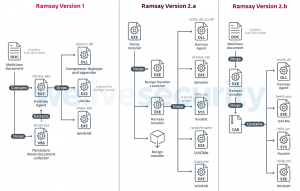 An installer (lmsch.exe) is then executed (earlier versions instead used an agent, netwiz.exe) that then deploys various modules enabling various capabilities.
An installer (lmsch.exe) is then executed (earlier versions instead used an agent, netwiz.exe) that then deploys various modules enabling various capabilities.
These modules execute several of the core capabilities of the malware. They gather all existing Microsoft Word documents (and in more recent versions, PDF files and .ZIP archives) within the target file systems, allow for privilege escalation (via UACMe instances), collect screenshots, and scan for network shares and removable drives, which the malware then uses for its spreading mechanism.
Later versions of Ramsay included a rootkit spreader. This spreader as acts a file-infection mechanism and changes the structure of benign Portable Executable (PE) files to embed malicious Ramsay artifacts. These are then triggered upon host file execution.
“The spreader is highly aggressive in its propagation mechanism, and any PE executables residing in the targeted drives would be candidates for infection,” said researchers. “This assesses the relationship between Ramsay’s spreading and control capabilities showing how Ramsay’s operators leverage the framework for lateral movement, denoting the likelihood that this framework has been designed to operate within air-gapped networks.”
Other Features
Ramsay also implements several persistence methods, including setting a scheduled task to persist after reboot and executing components as service dependencies. The most notable persistence method however is what the researchers call “Phantom DLL Hijacking.” This method abuses the fact that many Windows applications use outdated dependencies not strictly necessary for the functionality of the application itself – allowing attackers to leverage malicious versions of these dependencies.
“This persistence technique is highly versatile, enabling Ramsay agents delivered as DLLs to fragment their logic into separated sections, implementing different functionality tailored for the subject processes where the agent will be loaded,” said researchers. “In addition, the use of this technique makes detection more difficult, since the loading of these DLLs into their respective processes/services won’t necessarily trigger an alert.”
Researchers also noted that, unlike most conventional malware, Ramsay does not have a network-based command-and-control (C2) communication protocol, and does not attempt to connect to a remote host for communication purposes: “Exfiltration of these artifacts is done via an external component that we haven’t been able to retrieve,” they said.
Researchers said that Ramsay continues to be under active development, particularly in its scanning of machines susceptible to various exploits. Newer versions of the toolkit for instance sniff out machines within the compromised host’s subnet that are susceptible to the EternalBlue SMBv1 vulnerability.
“Developers in charge of attack vectors seem to be trying various approaches, such as old exploits for Word vulnerabilities from 2017, as well as deploying trojanized applications potentially being delivered via spear-phishing,” said researchers.
Inbox security is your best defense against today’s fastest growing security threat – phishing and Business Email Compromise attacks. On May 13 at 2 p.m. ET, join Valimail security experts and Threatpost for a FREE webinar, 5 Proven Strategies to Prevent Email Compromise. Get exclusive insights and advanced takeaways on how to lockdown your inbox to fend off the latest phishing and BEC assaults. Please register here for this sponsored webinar.












